When it comes to fortifying your organization’s cybersecurity, identifying vulnerabilities is a crucial first step. Vulnerability assessments (VA) and penetration testing (PT) are two methods commonly used to identify and address these security gaps. While both approaches aim to identify flaws, their scope, depth, and processes differ significantly. In this blog post, we’ll break down the differences between VA and PT, helping you understand which one—or combination—best suits your organization’s needs.
What Is Vulnerability Assessment?
A vulnerability assessment is a systematic, automated process designed to identify and prioritize security weaknesses across digital assets, networks, systems, applications, and cloud environments. This method typically offers a broad overview of potential security gaps, helping you pinpoint areas of concern that may require further attention.
How It Works:
Vulnerability assessments use automated tools to scan for known vulnerabilities such as unpatched software, configuration issues, or system weaknesses. The process can involve several types of scans, including web, application, and network scans.
Purpose:
The goal of a VA is to identify and categorize security flaws, providing recommendations for remediation to enhance system security.
Limitations:
While effective at highlighting potential issues, vulnerability assessments do not simulate real-world attacks. Therefore, they may not reveal how these vulnerabilities could be exploited by attackers.
What Is Penetration Testing?
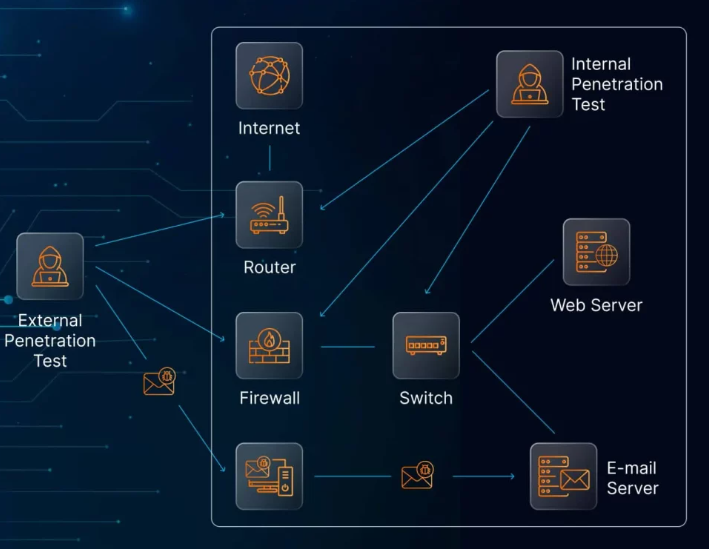
Penetration testing, on the other hand, is a more thorough, hands-on approach to identifying vulnerabilities. This method involves ethical hackers (penetration testers) simulating real-world cyberattacks to exploit weaknesses in an organization’s systems, networks, or web applications.
How It Works:
Penetration testing combines manual techniques with automated tools to simulate various attack vectors. The aim is to exploit weaknesses and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, mimicking the tactics used by real hackers.
Purpose:
The goal of a penetration test is to identify vulnerabilities, assess how they could be exploited in a real attack, and provide actionable recommendations for strengthening security defenses.
Limitations:
Penetration testing is resource-intensive and time-consuming. While it provides an in-depth analysis of security weaknesses, it may be more expensive than vulnerability assessments.
Key Differences Between Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing
Understanding the differences between VA and PT is essential for deciding which method to use for securing your systems.
1. Scope and Depth of Analysis
- Vulnerability Assessment:
VA focuses on breadth rather than depth. It casts a wide net to identify potential vulnerabilities but doesn’t test how these vulnerabilities could be exploited. Vulnerability scanning tools are used to provide an initial layer of defense by flagging possible weaknesses. - Penetration Testing:
Penetration testing takes a deeper dive into specific areas, actively attempting to exploit vulnerabilities to demonstrate the potential impact of a real-world attack. It uncovers hidden flaws and provides a detailed view of how these vulnerabilities can be leveraged.
2. Methodology
- Vulnerability Assessment:
VAs rely heavily on automated tools that compare systems against known vulnerability databases. While this makes the process faster and more cost-effective, it may miss complex or hidden vulnerabilities. - Penetration Testing:
Penetration testing, in contrast, involves manual techniques supported by automated tools. Ethical hackers use their expertise to simulate real attacks in a controlled environment, uncovering flaws that automated scans might miss.
3. Outcome and Reporting
- Vulnerability Assessment:
VAs typically generate reports listing discovered vulnerabilities, categorized by severity, and offer remediation suggestions. These reports can be quite technical and may include false positives. - Penetration Testing:
Penetration tests deliver more comprehensive reports that not only detail vulnerabilities but also explain how they were exploited during testing. The report includes specific recommendations for strengthening security and provides a thorough review of the target environment.
4. Cost and Resource Requirements
- Vulnerability Assessment:
VA is usually more affordable and faster due to its automated nature. This makes it ideal for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets. - Penetration Testing:
Penetration testing requires more time, expertise, and resources, making it a more significant financial investment. However, it provides a much deeper and more targeted analysis of security flaws.
Combining Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT)
A combined approach, known as Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT), provides the benefits of both methods, offering a comprehensive solution to detect weaknesses early and evaluate the effectiveness of your security measures. By using VAPT, organizations can identify vulnerabilities with fewer false positives, ensuring that resources are used efficiently for remediation.
VAPT and Compliance Considerations
Many industries are subject to regulatory frameworks that require regular security testing to protect sensitive data and ensure operational resilience. Standards like PCI DSS, ISO 27001, GDPR, and DORA emphasize the importance of robust security practices, including vulnerability scans and penetration tests.
- PCI DSS: Requires regular vulnerability testing and annual penetration tests to protect payment card data.
- ISO 27001: Integrates vulnerability management into its information security standards.
- GDPR: Advocates for strong security measures to protect personal data.
- DORA and NIS2: Focus on operational resilience, urging financial and critical infrastructure sectors to assess and secure their ICT systems.
How VA and PT Support Compliance and Build Trust
Implementing both vulnerability assessments and penetration testing can help organizations meet regulatory requirements, manage risks effectively, and build trust with stakeholders.
- Proactive Risk Management: Identifies and addresses security vulnerabilities, reducing the likelihood of security incidents.
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensures compliance with legal and industry requirements.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Demonstrates to customers, partners, and regulators that your organization takes security seriously and is prepared to handle emerging threats.
Conclusion
Both vulnerability assessments and penetration testing play essential roles in securing your systems. Vulnerability assessments provide broad, ongoing monitoring to identify potential security flaws, while penetration testing offers in-depth analysis of how those flaws could be exploited in real-world scenarios.
Rather than choosing one over the other, it’s best to integrate both approaches into your cybersecurity strategy. When used together, vulnerability assessments and penetration tests help ensure a well-rounded, proactive defense, enabling your organization to stay ahead of evolving threats and protect critical assets effectively.