Cybersecurity is no longer just a technical concern; it’s a crucial aspect of business operations. Picture this: A single cyberattack disrupts your organization, compromising sensitive data, halting operations, and tarnishing your reputation. Now imagine that same incident affecting an entire industry or even a nation. This is the scale of risk that the NIS2 Directive aims to address.
NIS2 isn’t just another update to regulations; it’s a comprehensive framework that sets new standards for cybersecurity across the European Union (EU). It compels organizations to rethink their approach to security, ensuring robust protections and promoting accountability. Whether your business is in healthcare, finance, or another vital sector, NIS2 demands more than basic compliance – it requires a strategic overhaul of how cybersecurity is handled across your entire organization.
What is NIS2 and Why is it Crucial?
At its heart, the NIS2 Directive is about strengthening the cybersecurity infrastructure of Europe. It is a significant enhancement of the original NIS Directive, designed to better address the growing and evolving cyber threats that businesses face. NIS2 seeks to ensure that essential digital services remain resilient against cyber threats, preventing disruptions to critical services.
This directive isn’t just about defending against attacks; it focuses on preventing them in the first place. By implementing higher cybersecurity standards across the EU, NIS2 fosters a culture of proactive security. The goal is for information security to become embedded in the daily operations of organizations, with increased collaboration and information-sharing between EU member states.
Why NIS2 is Essential for Organizations
NIS2’s importance goes beyond mere legal compliance; it’s about building resilience in a world where cyberattacks are an inevitable reality. The directive extends its reach to sectors that were previously not covered, but which are equally essential to the stability of society and the economy.
For businesses, NIS2 signals a fundamental shift. Basic security measures are no longer enough. Instead, organizations need a comprehensive, top-down approach, involving everyone from IT staff to the C-suite. The directive elevates cybersecurity to a boardroom priority, ensuring that security strategies receive the attention and resources they need.
Core Objectives of NIS2
To fully grasp the impact of NIS2, it’s essential to understand its primary objectives:
- Wider Coverage: NIS2 broadens the range of sectors it covers, ensuring that no critical service is left unprotected.
- Stricter Security Standards: Organizations are required to adopt advanced cybersecurity measures tailored to their specific risks.
- Mandatory Incident Reporting: NIS2 sets strict requirements for reporting cybersecurity incidents promptly, facilitating quicker response and mitigation.
- Management Accountability: Top management is held directly accountable for cybersecurity, ensuring it is prioritized at the highest organizational levels.
- Enhanced Collaboration: NIS2 strengthens cooperation and information sharing among EU member states, improving the collective cybersecurity landscape.
How NIS2 Came About
The NIS2 Directive is the latest step in the EU’s ongoing effort to bolster cybersecurity across member states. It builds upon the original NIS Directive introduced in 2016, which established the first EU-wide cybersecurity rules. However, with the rapid digital transformation and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, it quickly became clear that a more robust framework was needed.
Adopted by the European Commission in 2022 and effective from 2023, NIS2 reflects extensive consultations with stakeholders and aims to address gaps in the previous legal framework. The directive is designed to modernize the EU’s legal tools to respond to emerging cybersecurity challenges and create a more resilient digital ecosystem.
Who is Affected by NIS2?
NIS2 applies to both public and private organizations that are essential to the societal and economic stability of the EU, including sectors like:
- Energy
- Transport
- Health
- Digital infrastructure
- Financial markets
- Water supply
- Public administration
- Space technologies
Additionally, key digital service providers such as search engines, cloud services, and online marketplaces are also required to comply with NIS2’s security and notification standards.
Categorization of Organizations
NIS2 divides organizations into two categories:
- Essential Entities: These include critical sectors like hospitals and energy providers, which face the most stringent compliance requirements.
- Important Entities: Sectors like food supply and postal services, which have somewhat less demanding obligations.
What Does NIS2 Require?
NIS2 lays out a set of obligations designed to elevate the overall cybersecurity level of essential and important entities across the EU:
- Risk Management: Member states must regularly assess the risks associated with their networks and systems and implement comprehensive cybersecurity risk management measures.
- Incident Reporting: Organizations must report significant incidents within 24 hours and submit a detailed follow-up report within 72 hours.
- Supply Chain Security: NIS2 emphasizes securing the entire supply chain, requiring organizations to evaluate the cybersecurity practices of their suppliers.
- Leadership Accountability: Top management must oversee and ensure compliance with cybersecurity protocols, with penalties for non-compliance.
- Operational Continuity: Critical services must maintain operations during and after a cyber incident, with ongoing exercises and coordination with national and EU authorities.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
NIS2 introduces stronger enforcement measures to ensure compliance across all covered entities. Competent authorities in each member state can conduct audits, request detailed reports, and issue binding instructions for improving security. Penalties for non-compliance are severe:
- Financial Penalties: Fines for essential entities can be as high as €10 million or 2% of global turnover. For important entities, fines can reach €7 million or 1.4% of global revenue.
- Reputational Damage: Public disclosure of non-compliance can significantly damage an organization’s reputation, undermining trust with stakeholders and customers.
Timeline for NIS2 Implementation
- By October 2024: Member states must transpose NIS2 into national law.
- 2024-2025: National authorities will issue guidelines and frameworks to help organizations comply.
- Late 2025: Essential and important entities must demonstrate initial compliance, with enforcement actions starting soon after.
How to Prepare for NIS2 Compliance
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Evaluate your organization’s critical assets and identify potential vulnerabilities, including those within your supply chain.
- Update Cybersecurity Policies: Align your cybersecurity policies with NIS2 requirements, including incident response plans and security protocols.
- Implement Proactive Security Measures: Strengthen your network and systems with tools like multi-factor authentication, monitoring, and system updates.
- Establish Incident Reporting Protocols: Develop clear procedures for reporting incidents, ensuring compliance with the 24-hour reporting requirement.
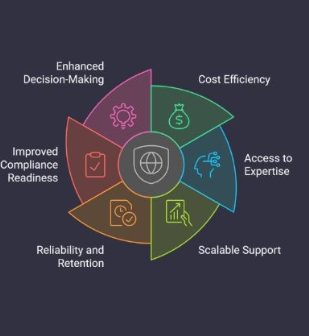
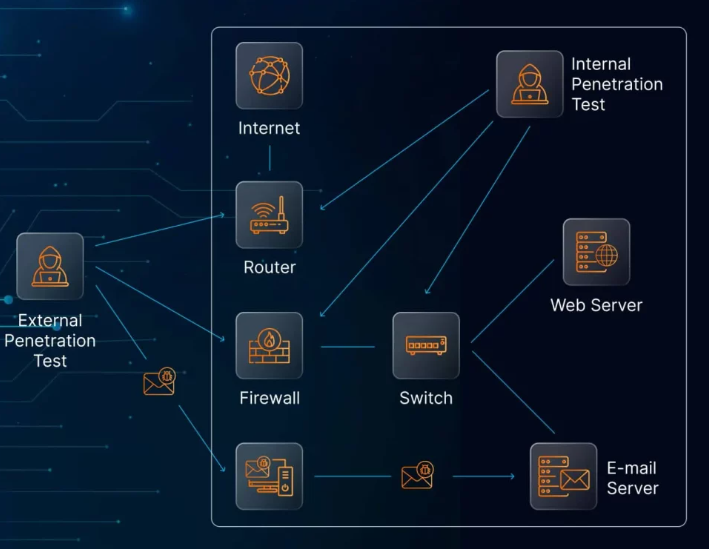
- Partner with Cybersecurity Experts: Consider working with external cybersecurity providers to help you navigate the complexities of compliance and stay updated on regulatory changes.
- Ensure Continuity: Test your business continuity plans regularly to ensure your organization can continue operating during and after an incident.
Conclusion
The NIS2 Directive marks a new era in cybersecurity, setting higher standards for resilience and accountability. It’s not just about avoiding penalties but about safeguarding your organization’s critical operations and maintaining the trust of your stakeholders. Achieving compliance requires a strategic approach, utilizing advanced cybersecurity tools and expert guidance to ensure you meet the directive’s requirements while defending against evolving cyber threats.