As cybercrime continues to grow in both scale and sophistication, businesses of all sizes face increasing challenges in protecting their data and systems. By 2025, the cost of cybercrime is projected to reach a staggering $10.5 trillion annually, making cybercrime the third-largest economy globally. This alarming figure highlights the urgent need for companies to adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
In a world where the threat of cyberattacks is ever-present, businesses must decide whether to react to breaches after they occur or take proactive measures to prevent them. A proactive approach to cybersecurity involves anticipating and mitigating threats before they can escalate, helping to avoid the costly consequences of breaches. One of the most effective proactive strategies is cybersecurity training for employees, empowering them to recognize and combat potential threats before they turn into major issues.
In this post, we will delve into the concept of proactive cybersecurity and explain why investing in both proactive measures and training is an essential step for any organization looking to protect itself from cyber threats.
What is Proactive Cybersecurity?
No business is immune to cyber threats. As cybercriminals constantly refine their tactics, organizations must adapt and evolve their defenses to stay one step ahead. Proactive cybersecurity is a strategy that focuses on early detection and prevention of threats. Rather than waiting for a breach to happen, this approach aims to identify potential vulnerabilities, address them before they are exploited, and build a culture of awareness and preparedness.
By embracing proactive cybersecurity, organizations can reduce risks, safeguard digital assets, and maintain customer trust. This strategy not only helps businesses withstand emerging cyber threats but also ensures operational continuity in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Key Elements of Proactive Cybersecurity
A successful proactive cybersecurity strategy integrates several key components aimed at preventing attacks and enhancing organizational resilience. Here are the primary elements of a proactive cybersecurity approach:
Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment is the foundation of any proactive cybersecurity strategy. This process involves identifying potential weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications, evaluating the likelihood of various cyber threats, and determining their potential impact. By understanding the risks they face, businesses can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources to strengthen their security posture.
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence provides valuable insights into emerging cyber threats, helping businesses anticipate attacks before they occur. By analyzing data on potential malicious actors, businesses can gain advance knowledge about their tactics and take appropriate preventive measures. Threat intelligence helps improve security protocols, enhance response strategies, and better protect organizational assets.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring allows organizations to detect suspicious activity in real-time, ensuring that threats are addressed before they escalate. By observing network traffic, endpoint activities, and system logs, businesses can quickly identify potential risks and respond proactively. This round-the-clock monitoring reduces the chances of successful attacks and allows for immediate mitigation efforts.
Incident Response Planning
A well-structured incident response plan is essential for managing the aftermath of a security breach. Proactive planning involves creating strategies for responding to incidents quickly and effectively. These plans should cover all stages of an incident, from detection to recovery, ensuring that businesses can resume operations with minimal disruption.
Examples of Proactive Cybersecurity Measures
Several practical measures can be implemented to strengthen a business’s cybersecurity defenses. These include:
- Threat Detection: Continuous monitoring of network and system activities helps detect unauthorized access and malicious behavior, allowing for immediate intervention.
- Managed Security Services: Small and medium-sized businesses often benefit from outsourcing network monitoring and threat intelligence to specialized providers, ensuring continuous expert oversight.
- Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices is essential for reducing human errors, which are often the weakest link in security.
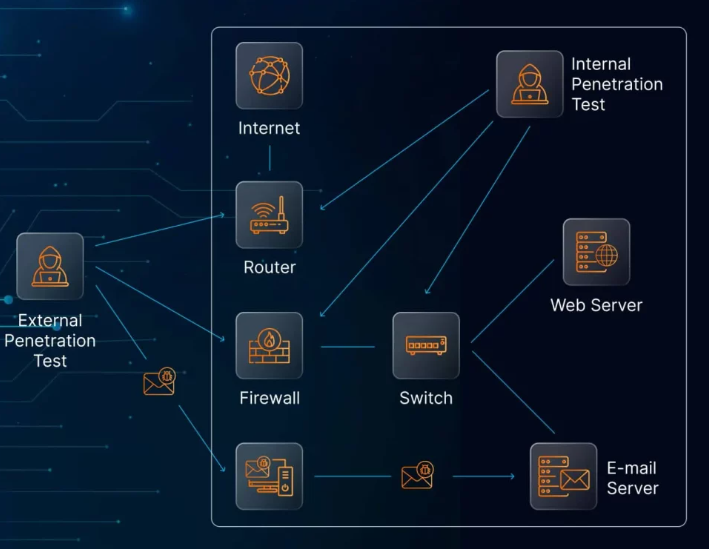
- Penetration Testing: By simulating cyberattacks, businesses can identify and fix vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them.
- Regulatory Compliance Audits: Regular audits help ensure that an organization’s security measures meet industry standards and comply with legal requirements.
Proactive vs. Reactive Cybersecurity
The main difference between proactive and reactive cybersecurity lies in when actions are taken. Reactive cybersecurity occurs after an attack has taken place. It involves responding to breaches, investigating their source, assessing damage, and recovering. While reactive measures are essential, they often come too late, leaving businesses vulnerable to significant damage.
Proactive cybersecurity, on the other hand, focuses on preventing attacks before they happen. By investing in preventive measures, businesses can reduce the likelihood of attacks, minimizing the financial and reputational impact. In today’s digital world, where threats are constantly evolving, a proactive cybersecurity strategy is not just a luxury – it’s a necessity.
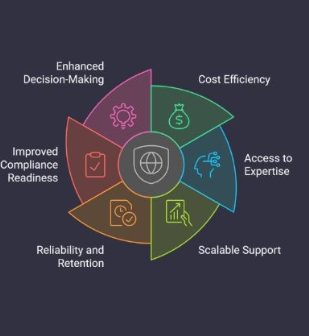
Benefits of Proactive Cybersecurity
Adopting a proactive approach to cybersecurity offers several key benefits:
- Reduced Risk and Downtime: Proactive measures help identify and mitigate threats before they cause damage, reducing downtime and operational disruption.
- Stronger Data Protection: By preventing cyber threats before they escalate, businesses can better safeguard their critical assets and customer data.
- Enhanced Reputation: Organizations that prioritize cybersecurity and demonstrate a commitment to protecting their data build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Proactive measures ensure that businesses comply with industry regulations, helping avoid legal issues and penalties.
- Improved Incident Response: With a well-prepared incident response plan, businesses can quickly recover from attacks and resume normal operations with minimal disruption.
How to Implement Proactive Cybersecurity
To successfully implement a proactive cybersecurity strategy, businesses must adopt a comprehensive and continuous approach. Here are the key steps to take:
- Leadership Commitment: Senior management must prioritize cybersecurity as a core part of the business strategy and cultivate a culture of security awareness across the organization.
- Risk Management: Conduct detailed risk assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
- Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats and adjust security measures accordingly.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring of network activities to quickly detect suspicious behavior and prevent attacks.
- Employee Training: Invest in regular cybersecurity training for all employees to ensure they understand their role in protecting company data and systems.
- Penetration Testing: Regularly conduct penetration testing to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Incident Response: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective reaction to any security breach.
The Role of Cybersecurity Training
Cybersecurity training is a vital component of any proactive strategy. It helps employees recognize and respond to potential threats, such as phishing scams and social engineering attacks. Given that human error is a leading cause of security breaches, training significantly reduces the risk of accidental exposure of sensitive information.
Training offers several benefits:
- Cost-effective: Training is a long-term investment that helps prevent costly security incidents.
- Regulatory Compliance: Training helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and stay compliant with security standards.
- Reduced Human Error: By educating employees on security best practices, the likelihood of mistakes that lead to breaches decreases.
- Improved Security Awareness: Employees become more vigilant and proactive in identifying and reporting suspicious activities.
The Cost of Cybersecurity Training
While cybersecurity training does incur costs, it should be viewed as a cost-saving measure in the long run. The financial impact of a cyberattack far outweighs the cost of training employees. For example, the average cost of a ransomware attack can run into the hundreds of thousands of dollars, while a well-trained workforce can significantly reduce the likelihood of such an attack occurring.
Investing in training not only protects your business from potential threats but also fosters a culture of cybersecurity awareness that strengthens your organization’s overall security posture.
Conclusion
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, proactive cybersecurity is essential for businesses to stay ahead of cyber threats. By implementing comprehensive security strategies, investing in continuous monitoring, and training employees to recognize and respond to threats, businesses can protect their data and systems from costly breaches. Proactive cybersecurity is not just a safeguard – it’s a strategic investment in your company’s long-term security and success.