In today’s interconnected world, the digital realm has become the battleground for businesses. Cyber attacks are not a matter of “if,” but “when.” Recent data breaches have laid bare the vulnerabilities of many companies, leaving them grappling with both financial and reputational damage. To protect your business, it’s crucial to learn from these breaches and adopt a solid cybersecurity strategy. Below, we explore key lessons and practices that can help you secure your digital assets.
Building a Robust Cybersecurity Framework
A well-structured cybersecurity plan is the cornerstone of your defense strategy. It should focus on safeguarding sensitive data from internal and external threats. A layered security approach that incorporates firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security is critical. Technology evolves rapidly, so it’s essential that your cybersecurity strategy does as well. Regular assessments and updates ensure that you are prepared to tackle emerging threats.
Empowering Your Employees as the First Line of Defense
Your workforce plays a vital role in your defense strategy. By providing your employees with thorough training on cybersecurity best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of breaches. Topics should include recognizing phishing attempts, understanding the dangers of social engineering, and maintaining good password hygiene. Regular phishing drills can help test their awareness and reinforce good habits. With the right knowledge, your employees can serve as a powerful shield against cyber threats.
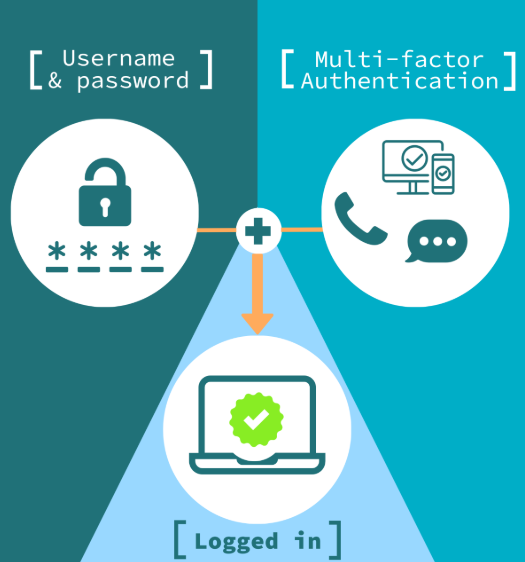
Securing Access: A Crucial Gatekeeper for Protection
One of the most common entry points for cybercriminals is compromised access credentials. To enhance security, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that users must provide multiple forms of verification before accessing critical systems. Limiting administrative privileges through privileged access management (PAM) and adopting passwordless authentication technologies like biometrics can further reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Swift Detection and Response: Minimizing the Impact of Attacks
When a cyber attack occurs, time is of the essence. To minimize damage, invest in tools and processes that allow for rapid detection and response. A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system can help monitor and analyze security events in real time, identifying potential threats before they escalate. An effective incident response team with clearly defined roles will ensure a coordinated and timely reaction when an attack is detected.
Reducing Your Attack Surface: A Proactive Approach to Security
Your attack surface consists of all the points through which attackers could potentially enter your network. By regularly assessing and managing this surface, you can identify and eliminate vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing will help pinpoint weak spots in your systems. Additionally, encouraging ethical hackers through bug bounty programs can uncover hidden flaws that could be targeted by malicious actors.
Sharing Threat Intelligence: Collective Defense in Action
Cybersecurity is not a solitary task. By collaborating with industry peers and participating in Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs), businesses can share valuable threat intelligence. This collaboration enables you to stay updated on attack trends and emerging vulnerabilities, helping to build a stronger collective defense. Remember, sharing knowledge enhances everyone’s security posture and makes the digital world a safer place for all.
Preparedness is Key: Incident Response and Disaster Recovery
Even with all the right security measures in place, breaches can still occur. Having a well-defined incident response plan ensures that your team can act quickly to contain and mitigate an attack. Alongside this, a disaster recovery plan is essential for restoring critical systems and data in the event of a major disruption. Regular testing of these plans ensures that everyone knows their role and that your organization can recover swiftly and efficiently.
Adopting a Zero Trust Model: Always Verify, Never Trust
In today’s cyber landscape, the concept of “trust” is increasingly risky. A zero-trust security model, which requires continuous verification of every user, device, and application before granting access, helps to minimize risks. Implementing micro-segmentation further reduces the potential for lateral movement within your network, ensuring that any breach remains contained. By enforcing strict access controls and multi-factor authentication, you can safeguard your organization from the inside out.
Ensuring Supply Chain Security: Vigilance Beyond Your Organization
Your cybersecurity efforts must extend beyond your organization to include your supply chain. Regularly assess the security of third-party vendors and partners through audits and security questionnaires. Incorporating security clauses into contracts and conducting periodic reviews will help minimize the risk posed by external parties. Additionally, having a response plan in place for potential supply chain attacks will ensure that you are prepared to act swiftly if needed.
Conclusion: Ongoing Vigilance for a Secure Future
Cybersecurity is a continuous journey, not a one-time fix. By adopting a proactive, multi-layered approach that includes people, processes, and technology, you can strengthen your defenses against evolving cyber threats. Keep your security posture under constant review, stay informed about emerging threats, and invest in the latest technologies to stay one step ahead in the digital battlefield. With vigilance and the right strategies in place, you can protect your business and thrive in the digital age.