In today’s digital landscape, small businesses face growing cybersecurity threats. While you might assume hackers only target large corporations, small businesses are often more vulnerable due to limited security measures. Protecting your company doesn’t require a massive budget—just smart, proactive steps. Here’s how to safeguard your data and operations effectively.
1. Train Employees on Security Best Practices
Your team is your first line of defense. Teach employees to recognize phishing scams, avoid suspicious downloads, and report unusual activity. Regular training reduces the risk of accidental breaches caused by human error.
2. Strengthen Password Policies
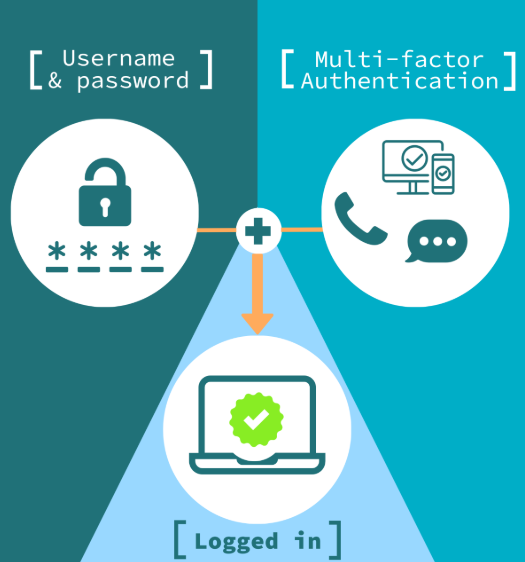
Weak passwords are an open door for hackers. Require employees to use complex passwords—ideally a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Better yet, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra verification step. A password manager can help staff manage logins securely.
3. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Cybercriminals exploit outdated software vulnerabilities. Enable automatic updates for operating systems, apps, and security software to patch weaknesses promptly.
4. Install Reliable Antivirus and Anti-Malware Tools
Free antivirus programs offer basic protection, but paid versions provide stronger defenses against ransomware, spyware, and other threats. Invest in trusted security software with real-time scanning and firewall protection.
5. Implement a Backup Strategy
Data loss from cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters can devastate a business. Automate backups and store copies both locally and in the cloud for redundancy. Test restores periodically to ensure data can be recovered quickly.
6. Secure Your Wi-Fi Network
An unsecured Wi-Fi network is a hacker’s playground. Use WPA3 encryption, change default router passwords, and create a separate guest network to keep business data isolated.
7. Restrict Access to Sensitive Data
Not every employee needs access to all company files. Follow the principle of least privilege, granting access only to those who require it. Regularly audit permissions and revoke access when roles change.
8. Be Wary of Phishing and Suspicious Links
Teach employees to scrutinize emails and avoid clicking on unknown links or attachments. Verify sender addresses and look for signs of phishing, such as urgent requests for sensitive information.
9. Protect Your Website
If your business has a website, ensure it uses HTTPS encryption to secure data transfers. A web application firewall (WAF) can block malicious traffic, and regular backups help recover quickly from attacks.
10. Develop an Incident Response Plan
Even with precautions, breaches can happen. A clear response plan helps minimize damage. Define steps for containment, communication, and recovery, and conduct drills so employees know how to act.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity isn’t a one-time task—it requires ongoing vigilance. By adopting these strategies, small businesses can reduce risks, protect customer trust, and avoid costly disruptions. Start strengthening your defenses today to ensure long-term success.
Need expert guidance? Consider consulting an IT security professional to tailor a protection plan for your business.