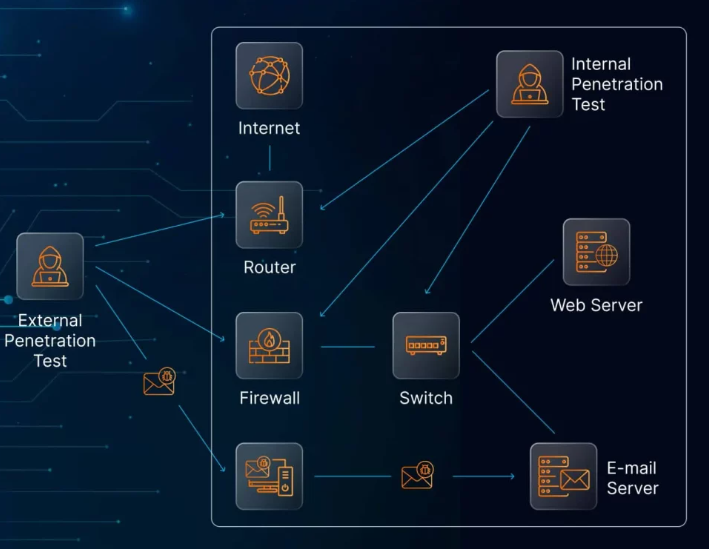
As businesses continue to integrate digital technology into every aspect of their operations, they become increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. Two terms frequently discussed when it comes to safeguarding digital assets are “cybersecurity” and “cyber resilience.” While they are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct approaches to protecting an organization’s data and infrastructure. Let’s dive into the differences between these two concepts and explore how they work together to ensure a comprehensive defense strategy.
What is Cyber Resilience?
Cyber resilience refers to an organization’s ability to prepare for, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents, such as data breaches and cyberattacks. Unlike traditional security measures that primarily focus on preventing attacks, cyber resilience emphasizes ensuring that business operations can continue with minimal disruption, even during and after a cyber event.
Key Components of Cyber Resilience:
- Preparedness: This involves creating processes and protocols that help anticipate and prepare for cyber threats.
- Detection: Implementing systems to identify and detect cyber threats in real-time.
- Response: Developing and executing a response plan to minimize the impact of incidents.
- Recovery: Ensuring a swift recovery to restore business operations and return to normalcy after an attack.
- Adaptation: Continuously improving and refining strategies based on lessons learned from previous incidents.
Benefits of Cyber Resilience:
A robust cyber resilience plan brings multiple benefits, including:
- Reduced Downtime: Quick recovery from cyber incidents minimizes disruptions and helps maintain operations.
- Enhanced Reputation: Businesses that recover swiftly demonstrate reliability and maintain customer trust.
- Cost Savings: Minimizing the impact of disruptions can lead to financial savings, as the costs associated with downtime and recovery are reduced.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting legal and industry standards is easier when an organization is well-prepared for cybersecurity threats.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that operate reliably during a cyber crisis can gain a stronger position in the market.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices and technologies designed to protect computer systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. It focuses on preventing unauthorized access, protecting against insider threats, and safeguarding the integrity of an organization’s assets. Cybersecurity strategies are typically proactive, aiming to stop attacks before they happen.
Objectives of Cybersecurity:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users.
- Integrity: Safeguarding the accuracy and completeness of data and systems, preventing unauthorized alterations.
- Availability: Ensuring critical data and services are available to authorized users without disruption.
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users and systems to ensure authorized access.
- Non-repudiation: Ensuring that actions and transactions are recorded and cannot be denied after they occur.
- Risk Management: Identifying and managing risks related to cyber threats.
- Incident Response: Developing protocols to detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents.
Importance of Cybersecurity:
Cybersecurity is vital for protecting sensitive data like personal information, financial records, and intellectual property. A solid cybersecurity strategy helps prevent significant data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage, making it essential for any organization handling sensitive information.
Cyber Resilience vs Cybersecurity: Understanding the Difference
While both cybersecurity and cyber resilience aim to protect organizations from cyber threats, their focus and methods differ. Cybersecurity primarily focuses on prevention, stopping attacks before they happen, using tools like firewalls, encryption, antivirus software, and access controls. On the other hand, cyber resilience focuses on maintaining business continuity and quickly recovering from an attack if one occurs.
In simple terms:
- Cybersecurity acts as the first line of defense, safeguarding systems and data from cyber threats.
- Cyber resilience ensures that even if those defenses are breached, the organization can still operate and recover quickly.
The Relationship Between the Two:
Cybersecurity and cyber resilience complement each other. While cybersecurity works to prevent breaches, cyber resilience ensures the organization can continue functioning during and after a security event. A well-rounded approach integrates both, allowing businesses to prevent, detect, and recover from cyber incidents.
Cyber Resilience Addresses Cybersecurity Limitations:
Cybersecurity, no matter how advanced, cannot guarantee 100% protection. New vulnerabilities emerge, and sophisticated attacks evolve. This is where cyber resilience comes into play. It prepares organizations for worst-case scenarios, ensuring they can quickly recover from disruptions and continue operating. Combining cybersecurity with cyber resilience creates a more robust defense, protecting the organization from both attacks and their aftermath.
Developing a Cyber Resilience Strategy
Creating an effective cyber resilience program involves several key steps:
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identify potential risks and weak spots in the organization’s systems and operations.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop clear policies and procedures for how to respond to cyber threats.
- Employee Training: Train staff on topics such as recognizing phishing attempts, using secure remote work practices, and implementing multi-factor authentication.
- Cybersecurity Testing: Regularly test your systems to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Improvement: As cyber threats evolve, so should your resilience plans. Regular updates and improvements are critical to staying ahead of the curve.
The Importance of Incident Response and Recovery
A well-structured incident response and recovery plan is essential for a resilient organization. It allows the company to quickly contain an attack, minimize damage, and restore normal operations. The first 48 hours following an attack are crucial, and a clear, tested response plan can help mitigate risks to the organization’s assets, reputation, and future.
Mitigating Damage and Financial Loss
Cyber resilience strategies go beyond just recovery; they also include long-term measures to minimize financial loss and damage. This may involve maintaining regular backups, having a disaster recovery plan, and investing in cyber insurance to cover potential losses.
Preparing for Future Cyber Threats
Staying ahead of cyber threats requires continuous monitoring, threat intelligence, and proactive defense strategies. Systems should be designed with redundancy in mind, and routine patching and updating should be standard practice. By building resilient systems, organizations can withstand attacks even if one component or network fails.
Balancing Cyber Resilience and Cybersecurity
A successful defense strategy requires balancing both cybersecurity and cyber resilience. Cybersecurity measures like firewalls, encryption, and access control are essential for protecting systems and preventing unauthorized access. However, since no defense is foolproof, cyber resilience provides the backup plan, ensuring the organization can recover quickly if an attack breaches its defenses. Combining both approaches helps organizations minimize risks, maintain business continuity, and protect sensitive data.
The Future of Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience
As cyber threats continue to evolve in both sophistication and frequency, organizations will need to adapt by taking an integrated approach to defense. While cybersecurity remains crucial for building strong defenses, cyber resilience will become even more vital as businesses acknowledge that some security breaches are inevitable. Investing in advanced threat detection, continuous monitoring, and employee training will be key to future success. Moreover, fostering a culture of resilience, where employees are prepared to act swiftly during an attack, will help organizations maintain operational continuity and gain a competitive advantage.