The financial technology landscape is transforming rapidly, with fintech companies at the forefront of innovation in digital payments, investment platforms, and online banking. But with increased convenience and connectivity comes heightened exposure to cyber threats. These companies manage vast amounts of sensitive data, making them an attractive target for cybercriminals seeking financial gain or system disruption.
To combat these threats, fintech businesses must prioritize cybersecurity as a fundamental component of their operations. One of the most effective strategies in this space is penetration testing—a controlled method of exposing security flaws before malicious actors do. Let’s explore why penetration testing matters in fintech, what areas require attention, and how it supports both compliance and trust.
Understanding the Security Landscape in Fintech
Fintech companies face unique security pressures due to the nature of their services. Handling financial transactions, storing customer information, and integrating with external systems create multiple potential entry points for attackers. Below are some of the key risks that set the fintech sector apart:
- Financial Data Is Highly Valuable: Hackers are drawn to financial platforms because the data involved—payment details, account information, transaction history—has immediate value on the black market.
- Strict Regulatory Expectations: Organizations must adhere to rigorous standards like PCI DSS, PSD2, and ISO 27001. Falling short can lead to penalties, lawsuits, and damaged credibility.
- Cloud and API Dependencies: Many fintech solutions rely on cloud-based infrastructure and third-party APIs, which add layers of complexity and increase exposure to configuration errors or insecure integrations.
- Third-Party Risk Exposure: A vulnerability in a partner service can compromise the entire fintech ecosystem. This includes payment processors, banking APIs, or customer verification tools.
To stay secure, fintech organizations must move beyond passive defenses and engage in proactive testing to uncover vulnerabilities before they’re exploited.
How Penetration Testing Supports Fintech Cybersecurity
Penetration testing involves simulating cyberattacks to uncover exploitable flaws in a company’s infrastructure. Unlike automated scans that detect known issues, pen tests attempt to exploit weaknesses using the same techniques as real-world attackers.
For fintech, this means:
- Locating weaknesses in applications, databases, APIs, and cloud configurations
- Evaluating the resilience of systems to different attack types, including social engineering
- Demonstrating security compliance with industry frameworks
- Offering practical recommendations for remediation and future prevention
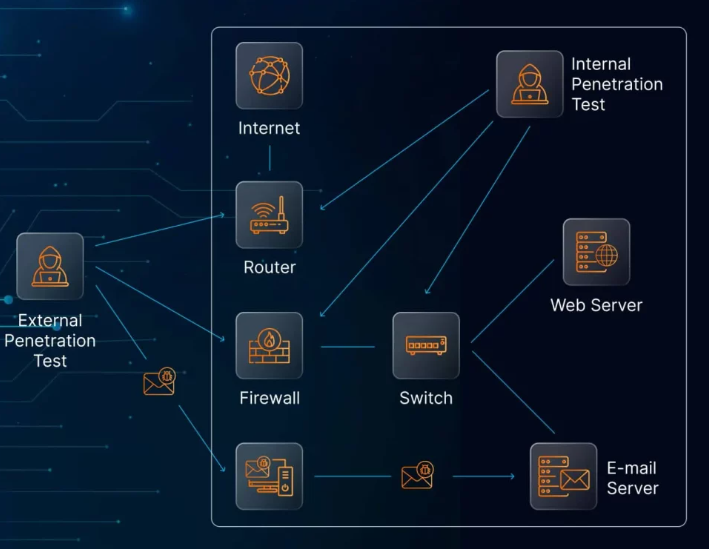
A complete test involves multiple phases, including planning, reconnaissance, exploitation, and reporting. Reputable cybersecurity teams—especially those with certifications like CREST or OSCP—are best equipped to carry out this kind of testing. After the initial assessment, a follow-up test is conducted to confirm that vulnerabilities have been resolved without introducing new ones.
Key Areas to Assess in Fintech Penetration Tests
Effective penetration testing for fintech companies involves a targeted approach across various attack surfaces. Here are the main components to focus on:
1. Web and Mobile Applications
These platforms are central to the user experience but often harbor risks such as:
- Weak or broken authentication controls
- Insecure data storage practices
- Vulnerable API endpoints
- Poor session management
Regular testing of application logic and infrastructure ensures that attackers cannot bypass security or access customer data.
2. Cloud Infrastructure
Fintech platforms often operate in cloud environments, where configuration errors can lead to serious breaches. Testing identifies:
- Insecure storage settings
- Poor access control policies
- Gaps in encryption implementation
These checks help ensure data remains protected across distributed systems.
3. Transaction Systems
Payment flows are a prime target for fraud. Pen testing should assess:
- The risk of transaction interception
- Compliance with data protection regulations like PCI DSS
- The effectiveness of anti-fraud detection mechanisms
These efforts help preserve the integrity of customer payments and financial operations.
4. API Security
APIs facilitate communication between services but also pose risks if improperly secured. Testing focuses on:
- Authorization bypass vulnerabilities
- Overexposed data endpoints
- Missing rate limits that could lead to denial-of-service scenarios
Proper API testing ensures that backend systems are not easily manipulated or compromised.
5. Network Segmentation
To protect sensitive data, fintech companies often segment their networks. This prevents attackers from moving freely if one system is breached. Testing evaluates:
- The effectiveness of segmentation policies
- Whether firewall rules block unauthorized access
- Resistance to lateral movement techniques
Proper segmentation reduces the attack surface and is essential for regulatory compliance.
6. Human Factors
Employees remain a common target for phishing and insider threats. Penetration tests may simulate social engineering attacks to evaluate:
- Susceptibility to credential theft
- Strength of access controls
- User behavior in response to suspicious communications
These simulations highlight areas where security awareness training is needed.
Benefits of Penetration Testing in Fintech
Security testing provides far more than compliance checkboxes. For fintech businesses, the advantages include:
- Avoiding Financial Loss: Identifying issues early reduces the chance of fraud or service disruptions.
- Supporting Compliance Efforts: Testing helps meet the requirements of frameworks like PCI DSS and ISO 27001.
- Building Customer Confidence: Clients are more likely to trust a platform that takes their data security seriously.
- Staying Ahead of Threats: The cyber threat landscape evolves rapidly. Regular testing ensures defenses adapt accordingly.
Fintech businesses should treat penetration testing as an ongoing process, particularly after introducing new features, launching integrations, or migrating systems.
Final Thoughts
The fintech sector continues to reshape global finance, offering faster, more efficient ways to manage money. But innovation also brings risk. In an industry built on trust, failing to safeguard data can have lasting consequences.
Penetration testing equips fintech companies with the insights they need to strengthen their defenses, demonstrate regulatory commitment, and ensure customer data remains secure. By embedding this practice into their cybersecurity strategy, these companies not only protect their digital assets—they build long-term resilience in a rapidly changing threat landscape.