As we move further into 2024, the world of cybersecurity is growing more complex, with cyberattacks evolving at an alarming rate. One concerning statistic: phishing attacks spiked by 61% last year. Despite the rising threats, you don’t need to feel helpless. Understanding common types of cyberattacks and knowing how to defend against them can make all the difference in safeguarding your personal and business data.
Phishing: Don’t Fall for the Trap
Phishing is one of the most prevalent types of cyberattacks. These attacks trick individuals into giving up sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, or personal data. Cybercriminals often pose as legitimate organizations, like your bank, a social media site, or even government bodies, to deceive you. With increasingly sophisticated tactics, these scams can be tough to spot, as attackers often use personal details to make their messages look more credible.
How to Defend Against Phishing:
Always be cautious when receiving unsolicited emails or messages. Avoid clicking on any links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. Before entering personal information on a website, double-check the URL and ensure it’s legitimate. Look out for red flags, such as poor grammar, urgent demands, or offers that seem too good to be true. Consider using anti-phishing tools or setting up filters to automatically block suspicious emails.
Ransomware: Don’t Let Them Hold Your Files Hostage
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that locks your files and demands payment, often in cryptocurrency, to release them. These attacks usually happen through phishing emails or by exploiting vulnerabilities in your software. The consequences can be severe, halting your operations and causing significant financial and operational setbacks.
How to Defend Against Ransomware:
Ensure that your data is regularly backed up to a secure external drive or cloud service, so you can restore it if needed. Keeping your software updated is essential to patch security vulnerabilities that ransomware may exploit. Use strong, unique passwords across all your accounts, and educate your employees on avoiding suspicious links and attachments. You may also want to explore advanced security solutions like endpoint detection and response (EDR) to detect and block ransomware before it spreads.
Malware: Protect Your Devices from Digital Threats
Malware refers to a range of malicious software, including viruses, worms, and Trojans, that can infect your devices, steal data, or damage systems. These threats often spread through infected websites, downloads, or even USB drives. Once inside your system, malware can cause data loss, system crashes, and even identity theft.
How to Defend Against Malware:
Install reputable antivirus and anti-malware software, and keep it updated. These programs can detect threats and prevent damage. Avoid downloading software from unknown or untrustworthy sources, and be cautious when opening email attachments. Regular scans of your devices can also help identify any malware lurking on your system.
Data Breaches: Lock Down Your Sensitive Information
Data breaches expose critical information like social security numbers, credit card details, and personal health records. These breaches can occur due to hacking, insider threats, or even human error. The fallout can be severe, ranging from identity theft and fraud to damage to your reputation.
How to Defend Against Data Breaches:
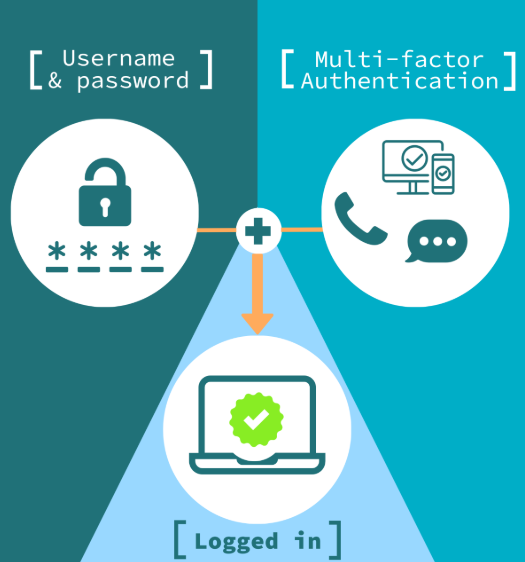
Use complex passwords and activate two-factor authentication (2FA) for an added layer of security. Regularly monitor your financial statements and credit reports for unusual activity. Encrypt sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, to make it more challenging for cybercriminals to access it. You should also implement a solid data breach response plan in case one occurs.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Keep Your Website Running Smoothly
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack floods your website or server with traffic to make it crash or become unavailable. These attacks can disrupt business operations and cause financial loss. Often, DoS attacks are launched by networks of infected computers, known as botnets.
How to Defend Against DoS Attacks:
If you manage a website or server, consider investing in Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) protection services. These can identify and neutralize attacks before they cause harm. Regular security audits can also help pinpoint vulnerabilities that could be exploited in an attack.
Zero-Day Attacks: Be Ready for the Unexpected
Zero-day attacks target vulnerabilities in software that the vendor isn’t aware of, making them especially dangerous since no fix is available yet. These attacks often come from highly skilled attackers such as cybercriminal groups or even nation-state actors.
How to Defend Against Zero-Day Attacks:
Always update your software as soon as patches are released, as these often address newly discovered vulnerabilities. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) can monitor your network for suspicious activity, while Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems help analyze security logs for potential threats.
Social Engineering: The Power of Manipulation
Social engineering is the manipulation of people into divulging confidential information or taking actions that compromise security. These attacks often rely on psychological tactics, such as impersonating a trusted authority figure or creating a sense of urgency. Social engineering can occur through email, phone calls, or even social media.
How to Defend Against Social Engineering:
Educate yourself and your employees about common social engineering techniques. Always verify the identity of anyone requesting sensitive information, even if they appear to be from a trusted source. Establish clear procedures for handling sensitive data, and be cautious when dealing with unsolicited requests.
Conclusion: Stay Vigilant, Stay Safe
As cyberattacks continue to evolve, staying protected requires proactive measures and constant vigilance. By understanding common threats like phishing, ransomware, malware, and more, you can implement strategies to defend against them effectively. Regular software updates, strong passwords, employee education, and robust backup practices are just a few ways to safeguard your data. Keep these strategies in mind, and you’ll be better prepared to tackle whatever the cyber world throws your way in 2024.