Unstructured data, unlike its structured counterpart, is what many employees across various industries interact with on a daily basis. This type of data is used for countless purposes and is shared widely within organizations. In reality, data needs to be easily accessible to drive collaboration and make the most out of it. However, as humans, we often end up storing these files in chaotic folder systems, and while we like to share data, we also tend to hoard it in places that aren’t always accessible or organized. For instance, many people might download a file from SharePoint, email it to a colleague, and hope they can access it offline—while traveling or during a meeting, for example.
One of the main challenges in managing unstructured data is the sheer amount of data spread across various platforms, which is often called “data sprawl.” When companies experience high employee turnover, these files can become “orphaned,” with open permissions that are rarely monitored, leaving the system vulnerable to hacking and clogging up file shares. In fact, some file shares have seen over 70% of their data orphaned with open read/write permissions—posing a significant risk.
The Struggles of Managing Data Overload
Unstructured data is growing at an alarming rate, driven by new applications and technologies like high-resolution image processing and sensor networks that collect billions of data points. Add in the demands of large-scale AI models, and it’s no surprise that industry analysts predict unstructured data will grow by 25-30% annually. By 2025, it is estimated that global data capacity will reach 180 zettabytes, with unstructured data comprising around 80% of that total. The growth isn’t expected to slow down anytime soon, further complicating data management.
The Growing Importance of Data Management
Companies are increasingly recognizing that data is one of their most valuable assets. The 2024 Wavestone survey highlights some key trends over the past five years:
- The number of businesses driving innovation through data increased from 59.5% to 77.6%.
- Companies managing data as a core asset grew from 39.5% to 49.1%.
- Organizations fostering a data-driven culture more than doubled, from 20.6% to 42.6%.
As data becomes more critical, companies must protect it as a high-value asset, adding another layer of complexity to data management.
Efficient Strategies for Managing Unstructured Data
So, how can organizations manage this ever-growing, unruly data more effectively? Here are some strategies that have proven useful:
At a recent AI conference, I spoke with the Chief Data Scientist at a major bank, who emphasized the importance of starting every data project with an assessment of metadata. He referred to metadata as the “DNA” of the data, and I agree with his view. Understanding the metadata is an excellent way to inventory data and prepare for large-scale management. For optimal management, a solution should:
- Scale easily by utilizing a flexible VM-based architecture.
- Support multi-threaded processing for efficient scanning.
- Have robust connectors to handle petabytes of data in weeks instead of months.
- Integrate well with cloud sources and applications to manage the influx of unstructured data.
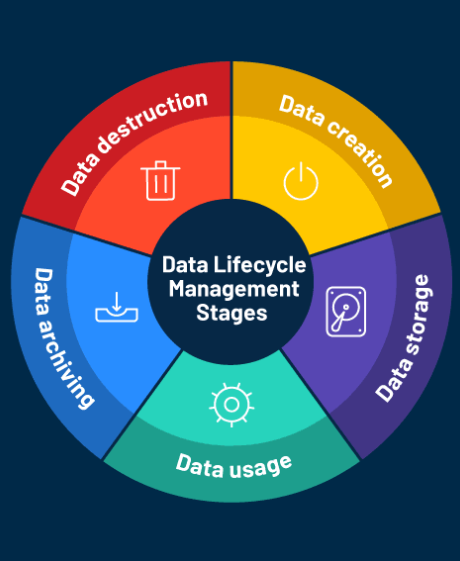
Once the data has been inventoried, remediation can begin. Organizing the data by classification allows automated policies to clean up unnecessary data (like redundant, obsolete, or trivial files), archive inactive data, and identify data for AI models. It also helps with cloud migration, improving security, and adjusting access controls. The right solution will include:
- An easy-to-use enterprise-grade interface.
- Comprehensive reporting tools.
- API connections for integration with reporting systems.
- Detailed audit trails for transparency.
- Automated workflows, with notifications and approval processes.
With this “data cleanup,” you can significantly reduce the data set—typically trimming it down to 10-20% of the original size—making it more manageable for further analysis. This step often leads to substantial savings on storage, backup costs, and preparation for AI models. It also helps with cloud transformations and reduces security risks.
The final step focuses on full governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) mitigation, which requires detailed content analysis. The solution for this step should include:
- Advanced AI and machine learning to improve accuracy.
- Scalable architecture for handling large volumes of data.
- Automated workflows for efficiency.
- Comprehensive audit trails for compliance.
By breaking data management into these three steps, organizations can significantly reduce the complexity, time, and costs associated with managing unstructured data, making it a more manageable and secure asset.