Introduction to Data Governance
Data governance is essential for managing and securing data, ensuring it is accurate, accessible, and safe. This practice is vital for maintaining data quality, meeting legal requirements, and supporting decision-making. It is especially critical for enterprises, insurance companies, and law firms, where solid data governance ensures smooth operations and regulatory compliance.
Identifying Resource Limitations
Before diving into a data governance strategy, it’s important to recognize the constraints you face. Here’s how to start:
- Assess Available Staff: Identify who in your organization can contribute to data governance roles, even if it’s on a part-time basis.
- Review Financial Limitations: Understand your budget and allocate resources to the most urgent needs.
- Evaluate Technology Infrastructure: Check your existing tools and systems to see which can support data governance.
Evaluating Current Data Governance Status
When resources are tight, evaluating your current data governance status is crucial. Follow these steps to get a clear picture:
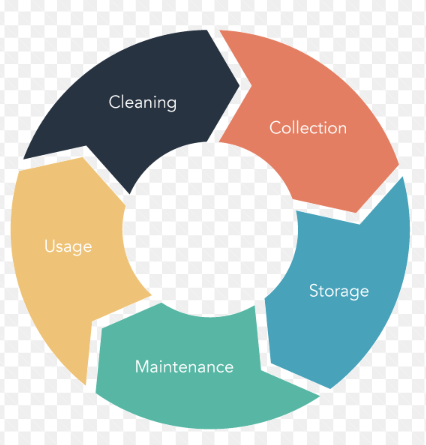
- Conduct a Data Audit: This helps you understand the volume and nature of the data you need to govern.
- Evaluate Data Quality: Identifying areas of poor data quality allows you to focus your efforts on the most pressing issues.
- Review Existing Processes: Look at your data management practices, from input to storage and retrieval, to spot inefficiencies.
- Identify Key Stakeholders: Recognize the key people involved in data governance to ensure effective task delegation and alignment with your goals.
- Assess Current Tools: Take stock of the tools and platforms you currently use for managing data, and assess their effectiveness.
Prioritizing Your Data
Not all data is equally important. To make the most of your resources, prioritize based on:
- Categorizing Data: Organize your data by its importance and sensitivity.
- Critical Data: Data necessary for business operations or compliance.
- Sensitive Data: Personally identifiable information (PII) or financial records.
- Non-Critical Data: Data whose loss or compromise would not significantly affect operations.
- Compliance Needs: Ensure your data governance practices meet relevant regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA.
Creating a Data Governance Framework
To build an effective framework with limited resources, follow these steps:
- Form a Data Governance Team: Assemble a team with representatives from different departments, such as IT, legal, and compliance.
- Define Roles: Clearly outline each team member’s responsibilities to avoid confusion.
- Establish Policies and Procedures: Create guidelines that address data quality, security, and compliance.
- Appoint Data Stewards: Assign people to oversee data management and ensure governance standards are followed.
- Create a Data Catalog: Document data sources, ownership, and classifications to improve data tracking and management.
Gathering Feedback to Improve Practices
To ensure your data governance strategy remains effective, collect feedback from users. This can help identify any areas that need improvement. Surveys or focus groups with stakeholders are excellent ways to gather insights.
Maximizing Technology on a Budget
You can optimize your data governance without breaking the bank by using cost-effective technologies:
- Open-Source Tools: Explore open-source platforms like Apache Atlas or Talend for data governance.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud platforms provide scalability and flexibility for governance efforts.
- Automation: Use automated tools to monitor data quality and compliance, reducing manual work.
- Data Visualization Tools: Utilize free or affordable tools like Google Data Studio or Tableau Public to visualize and communicate data insights.
- Data Integration Tools: Use tools such as Apache Nifi or Microsoft’s Power Automate to streamline data workflows.
Incorporating data quality tools into your strategy is crucial for maintaining clean, reliable data. Platforms like Congruity360 excel in automating data quality processes, ensuring data integrity even when resources are limited. Its scalability makes it an ideal choice for organizations with budget constraints, enabling effective governance practices.
Tracking Progress and Measuring Success
It’s essential to measure the effectiveness of your data governance efforts using key performance indicators (KPIs):
- Data Quality Metrics: Track improvements in data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensure ongoing adherence to regulations and internal policies.
- Data Usage: Monitor how data is being used across the organization to identify areas for improvement.
- Feedback: Use feedback from data users to refine your governance strategy.
Conclusion
Implementing an effective data governance framework is possible, even with limited resources. Start by prioritizing critical data, leveraging affordable technology, and fostering a culture of data stewardship. By continuously refining your practices, you’ll ensure your organization’s data remains valuable and secure.