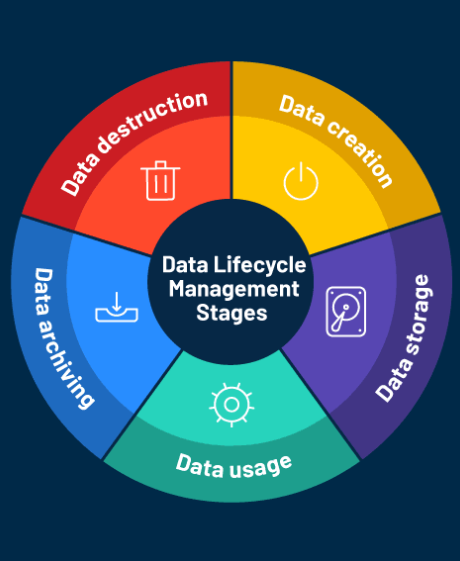
As global supply chains face increasing pressure, businesses are forced to reassess their approach to data storage. With rising tariffs inflating hardware and operational expenses, optimizing data storage has become essential for protecting margins, mitigating risk, and enhancing operational efficiency. Now more than ever, storage optimization plays a crucial role in maintaining business success.
The Hidden Costs of Data Storage
While companies often focus on obvious costs like labor and logistics, data storage expenses are quietly consuming a significant portion of enterprise budgets. These costs are only rising due to tariffs on hardware components, increasing cloud storage fees, and added charges for cross-border data transfers. This combination of factors is creating a perfect storm for IT and finance teams.
The Challenge: Making Storage Decisions Amid Economic Pressure
As economic pressures mount, many organizations are rethinking their storage strategies. Previously planned investments in storage refresh cycles, data center expansions, or even cloud repatriation are now under review. Tariffs are delaying these investments, while cross-border data transfer costs complicate global strategies.
For multinational companies, especially those involved in mergers and acquisitions, inherited data stores often include redundant or poorly classified datasets. These datasets are not only costly but also create compliance risks and slow down system performance.
The Solution: Data Classification and Strategic Storage Optimization
Optimizing storage begins with gaining visibility into your data. By implementing automated data classification and aligning storage tiers with the value of the data, organizations can reduce costs, ensure compliance, and improve resilience.
1. Classify Before Storing
Understanding your data and deciding what to keep is key to reducing storage costs.
- Automatically classify data based on sensitivity, business importance, and regulatory retention requirements.
- Identify and eliminate redundant, obsolete, or trivial (ROT) data by archiving or securely deleting it.
- Prioritize important and frequently accessed data for high-performance storage, while moving stale data to less expensive options.
2. Use Tiered Storage Strategies
Not all data needs to be stored at premium costs.
- Move infrequently accessed or lower-priority data to cheaper storage solutions or cold storage.
- Reserve hot storage (such as SSD-backed cloud or on-premise systems) for critical data that requires fast access.
3. Make Region-Specific Storage Decisions
Consider regional storage options to save on costs and comply with regulations.
- Store data within the same jurisdiction to minimize cross-border transfer fees and legal challenges, such as those imposed by GDPR or China’s PIPL.
- Avoid cloud egress fees by placing data in regions that are aligned with application workflows and user access needs.
4. Post-Merger Data Cleanup
Mergers and acquisitions often lead to an explosion of duplicated, outdated, and non-compliant data.
- Use data classification tools to sort inherited data and eliminate unnecessary storage.
- Consolidate systems and archive or delete redundant legacy datasets to reduce costs and minimize risk.
Why Storage Optimization Matters for Financial Strategy
With every gigabyte of data carrying a cost—and every border potentially adding a fee—storage optimization is no longer just an IT concern. It’s a financial strategy. By aligning your storage practices with modern classification standards and regional compliance requirements, you not only improve your IT efficiency but also protect your financial bottom line.
In today’s world, smart organizations are asking: “What is our data really worth, and what is it costing us?” The answer lies in smarter data management strategies.
Let’s explore how you can build a more cost-effective, efficient, and productive data strategy.