As businesses become more dependent on digital systems, network security threats are on the rise. Understanding these common risks and knowing how to prevent them is vital for protecting sensitive information, ensuring business continuity, and maintaining trust with clients and partners. From malware to insider threats, recognizing and addressing these threats is key to securing your network.
Common Network Security Threats
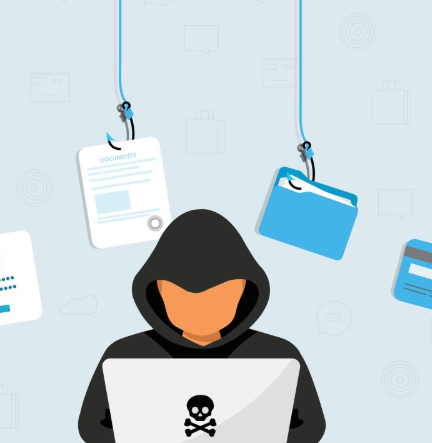
- Malware
Malware encompasses various types of harmful software, such as viruses, ransomware, worms, and spyware. These malicious programs can infiltrate systems to steal data, disrupt operations, or demand ransom payments to release data. - Phishing
Phishing attacks involve fraudulent emails or messages designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software. These attacks often appear to come from trusted sources, making them hard to detect. - Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks flood networks with excessive traffic, overwhelming resources and causing disruptions that render systems and websites inaccessible. - Insider Threats
Insider threats arise when employees or contractors misuse their access privileges to compromise security, whether intentionally (such as stealing data) or unintentionally (like clicking on a harmful link). - Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
In MITM attacks, hackers intercept communications between two parties to steal or alter data without either party realizing it. - Unpatched Vulnerabilities
Outdated software or systems that haven’t been updated or patched provide attackers with easy opportunities to exploit weaknesses in the network.
How to Mitigate These Threats
- Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Effective antivirus and anti-malware programs are essential for detecting and removing harmful software before it causes significant damage to your network. - Educate Employees
Regular training is crucial to help employees recognize phishing attempts, follow strong password practices, and adhere to cybersecurity policies. Human error remains a leading cause of network breaches. - Implement Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls help control network traffic, blocking unauthorized access, while intrusion detection systems can identify and alert you to suspicious behavior or potential threats. - Keep Systems Updated
Regularly update all software and systems with the latest security patches to eliminate vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might target. - Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Require MFA on all user accounts to add an additional layer of protection. This makes it much harder for attackers to access accounts, even if they have stolen login credentials. - Monitor Network Activity
Ongoing monitoring of network traffic helps identify unusual patterns and potential threats in real time, allowing you to respond swiftly to emerging issues.
Did You Know?
Around 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error. Regular employee training and awareness are essential in minimizing these risks and protecting your network.
By staying vigilant and applying these best practices, organizations can effectively safeguard their networks against common security threats and reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.