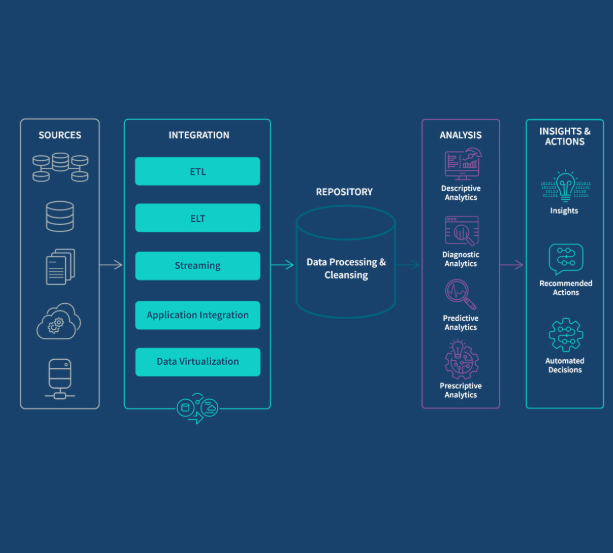
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are leveraging different types of data analytics to inform decisions and shape strategies. Among the most commonly used techniques are descriptive analytics and predictive analytics. While both provide valuable insights, they serve different purposes and are employed in various scenarios. Understanding the differences between these two approaches is essential for selecting the right strategy based on your business needs.
This blog will break down the key differences between descriptive and predictive analytics, explain how each one works, highlight their advantages and limitations, and explore their real-world applications.
What is Descriptive Analytics?
Descriptive analytics focuses on examining past data to identify patterns, trends, and insights. It is primarily used to summarize historical events to provide a clear picture of what has already happened. By analyzing past data, businesses can gain a better understanding of their operations, customer behavior, and overall performance.
Descriptive analytics typically involves using statistical tools and visualizations such as charts, graphs, and dashboards to present the data in a more accessible and understandable way. The primary goal is to provide actionable insights that help stakeholders make informed decisions.
How Descriptive Analytics Works
The process starts by gathering and cleaning historical data from multiple sources. Once the data is ready, statistical techniques are applied to identify trends and patterns. Measures such as mean, median, and standard deviation are commonly used. The results are then presented through data visualization tools to facilitate interpretation by stakeholders, which helps in decision-making.
Advantages of Descriptive Analytics
- Offers historical insights into business operations and relationships with customers.
- Helps identify areas of improvement by highlighting performance gaps.
- Assists in calculating return on investment (ROI) and tracking key metrics.
Limitations of Descriptive Analytics
- Provides a limited perspective since it only focuses on past data.
- Further analysis is needed to fully understand how the data can inform future strategies.
- Interpreting the data may require the expertise of specialists in the relevant domain.
Applications of Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics is used across various industries. For instance:
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient records to identify disease trends.
- Finance: Understanding market trends and investment performance.
- Retail: Segmenting customers and analyzing shopping behavior.
- Manufacturing: Monitoring production efficiency and identifying bottlenecks.
By examining historical data, businesses can identify trends that guide decisions and optimize future strategies.
What is Predictive Analytics?
Predictive analytics moves beyond merely understanding the past; it uses past and current data to predict future outcomes. This technique employs tools such as statistical modeling, machine learning algorithms, and data mining to identify patterns that can inform predictions about future events.
The aim is to empower organizations with insights that help them make informed, forward-thinking decisions. Predictive analytics is widely used in industries like retail, healthcare, and finance to forecast demand, customer behavior, and risk.
How Predictive Analytics Works
The process of predictive analytics starts with collecting and organizing data, which is then analyzed using statistical and machine learning techniques. These techniques help identify relationships, trends, and patterns. Based on the insights gained, predictive models are created, which are continuously tested and refined to ensure their accuracy.
Once these models are fully developed, they can be deployed to make predictions that guide decision-making.
Advantages of Predictive Analytics
- Provides scalable data modeling solutions applicable across various organizational levels.
- Enables self-service analytics, giving teams access to advanced insights.
- Helps automate decision-making, reducing the need for manual input.
- Can identify future trends and forecast potential challenges, which is crucial for industries like retail and healthcare.
- Improves accuracy in complex pattern recognition, leading to better predictions.
Limitations of Predictive Analytics
- Predictions are based on probabilities, so there’s always a margin of error.
- Consumer behavior and market dynamics are constantly changing, which may reduce the accuracy of the models.
- Requires ongoing updates and validation to ensure model accuracy over time.
Applications of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is widely used in several sectors:
- Manufacturing: Predicting equipment failure and scheduling maintenance.
- Transportation: Forecasting traffic patterns and optimizing delivery routes.
- Insurance: Determining risk factors, setting premiums, and detecting fraud.
- Retail: Anticipating customer buying behavior and demand during peak seasons.
In each of these sectors, predictive models help businesses stay ahead by anticipating challenges and opportunities.
Key Differences Between Descriptive and Predictive Analytics
While both types of analytics provide valuable insights, their objectives and methodologies differ significantly:
- Purpose: Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding what has happened in the past, whereas predictive analytics is designed to forecast what may happen in the future.
- Methodology: Descriptive analytics relies on statistical analysis and visualization to summarize data, while predictive analytics uses more complex techniques like machine learning, data mining, and high-level statistics to predict future outcomes.
- Scope: Descriptive analytics provides insights into historical data, helping businesses optimize current operations. Predictive analytics, on the other hand, helps organizations make proactive decisions by predicting future trends.
Final Thoughts
Descriptive and predictive analytics both play important roles in an organization’s data strategy. Descriptive analytics helps businesses understand past performance and identify patterns, while predictive analytics enables organizations to anticipate future trends and make data-driven predictions. By integrating both approaches, businesses can leverage data to optimize current operations and plan for the future.
Understanding when to use each type of analytics will help organizations unlock the full potential of their data, driving smarter decision-making and better business outcomes.