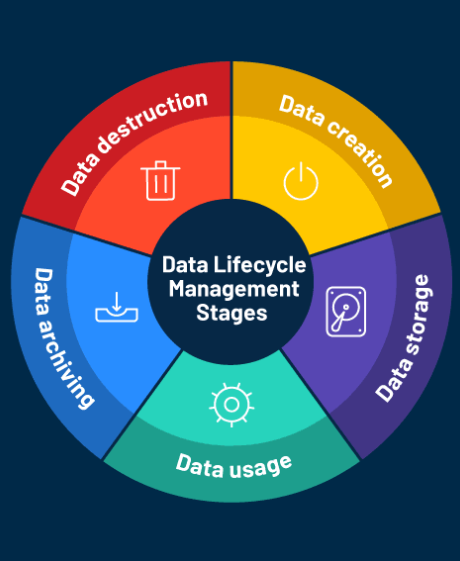
Data retention is an essential but often complex task that businesses of all sizes must face. As the volume of data generated by companies continues to rise, managing it has become increasingly difficult. The process can feel overwhelming, unclear, and cumbersome—but it doesn’t have to be.
So, what exactly is data retention, and why does it matter? Simply put, data retention refers to the practice of determining what data should be kept and for how long, as well as what should be discarded. This process is not only important for business intelligence but also crucial for data security and compliance with regulations. Implementing clear data retention policies can streamline this process and ensure that businesses remain compliant while protecting sensitive information.
Why Data Retention Policies Matter
Data comes in many forms and serves numerous purposes within a business. To ensure effective data management, companies should define what data needs to be retained and for how long. These guidelines are known as data retention rules, and they are a key component of any comprehensive data governance strategy. But why should businesses care about having these rules in place?
Simply put, it’s costly not to.
The adage “time equals money” rings especially true in the realm of data retention. Poor data management—whether from hoarding unnecessary data or failing to keep essential information—leads to inefficiency and increased storage costs. Additionally, various regulatory bodies require businesses to retain certain types of data for specific periods. For example, the New York Department of Financial Services mandates that insurers retain claim files for at least six years after the file has been closed. Non-compliance with these rules can result in hefty fines, and in legal situations, failure to retain discoverable material can lead to significant penalties.
However, it’s important not to overcompensate by retaining data indefinitely in an effort to cover all bases. While this may seem like a safe bet from a regulatory standpoint, it leads to unnecessary storage costs. Proper data retention rules help businesses identify data that no longer needs to be accessed frequently, allowing them to store it in more cost-effective ways or delete it altogether.
Key Considerations When Creating a Data Retention Policy
What Data Should Be Retained?
Data is central to the daily operations of any business, used for everything from customer insights to product development. With so much information constantly being generated, knowing what data is important to keep can be tricky. The answer varies depending on a company’s objectives, industry, and regulatory landscape. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Business Operations: Certain data is essential for everyday business functions, such as customer data, employee records, and sales performance analytics. Identifying this data helps improve decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Business Continuity: Data retention policies ensure businesses can access historical information in the event of system failures or disasters, keeping the organization running smoothly.
- Regulatory Requirements: Many industries are subject to strict regulations that require certain data to be kept for a set amount of time. Compliance with these laws ensures that businesses are prepared for audits or investigations.
- Legal Requirements: In the event of litigation or legal action, companies must retain relevant data to avoid penalties. Properly managing legal holds is crucial for protecting businesses from legal risks.
How Long Should Data Be Kept?
The duration for which data should be retained depends on its type and the applicable regulations. While some data needs to be kept for years, others may only need to be stored for a few months. Businesses must evaluate each type of data and determine the appropriate retention period, keeping in mind both business needs and legal requirements.
Where Is the Data Stored?
As the volume of data grows, so do the number of places it’s stored. Having a clear understanding of where data resides—whether on company servers, in the cloud, or within third-party systems—is essential for both security and compliance. It’s also important to note that some jurisdictions have specific regulations regarding where data can be stored and whether it can be transferred across borders.
Who Owns the Data?
Data ownership is a crucial aspect of data retention. Different departments within a company may own and be responsible for various types of data, so it’s important to ensure that the appropriate parties are involved in decisions regarding data retention and disposal. This oversight helps prevent the loss of important information and ensures that data is managed properly across departments.
The Importance of Automation in Data Retention
The key to managing data retention effectively is automation. Manual data management processes can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automation streamlines the enforcement of data retention rules across the organization, saving time, resources, and minimizing the risk of human error.
Automated systems help businesses consistently implement retention policies, ensuring compliance and reducing the burden on employees. Automated tools also allow businesses to quickly identify, classify, and handle data according to retention guidelines, freeing up staff to focus on more complex tasks. Additionally, automation can help businesses respond to legal holds quickly, ensuring that data is preserved as required without slowing down operations.
Conclusion
Data retention doesn’t have to be a daunting challenge. With a well-defined policy in place, businesses can manage their data efficiently, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect sensitive information. By understanding what data needs to be kept, how long it should be stored, and who is responsible for it, companies can streamline their data retention processes and reduce storage costs. With automation playing a key role in enforcing retention policies, businesses can focus on the more complex aspects of data management while maintaining compliance and security.