In today’s digital age, online identities have become central to how businesses operate. From accessing emails and social media accounts to managing online banking and business applications, credentials like usernames and passwords are the gateways to our digital lives. But what happens when these credentials are compromised? The consequences can be devastating for individuals and businesses alike. In fact, compromised credentials are one of the leading causes of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Businesses, particularly smaller ones, are at an increasing risk as attackers exploit weak or stolen credentials to infiltrate systems, steal sensitive data, and cause significant financial and reputational damage. A 2023 Verizon report highlighted that 49% of data breaches were due to compromised credentials, making the protection of digital identities more important than ever. In this post, we’ll explore how these attacks occur, their impact on your business, and the steps you can take to protect your organization.
The Many Ways Credentials Can Be Compromised
Credential compromise is a growing concern, with cybercriminals using various tactics to gain unauthorized access to systems. Understanding these methods is key to defending against them effectively.
Password Theft: A Common Weak Point
Weak, reused, or easily guessable passwords are prime targets for cybercriminals. Attackers often use methods like brute-force attacks, where they try countless password combinations, or dictionary attacks that exploit common passwords. Another prevalent method is credential stuffing, where stolen credentials from one site are used to gain access to accounts on other platforms.
The best defense against these attacks is to adopt strong password practices. Ensure all passwords are unique, long, and complex, containing a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid common passwords like birthdays or pet names, and consider using a password manager to generate and securely store these passwords.
Phishing: The Deceptive Lure
Phishing remains one of the most effective ways to steal login credentials. In these attacks, cybercriminals impersonate trusted entities such as banks or social media platforms and send deceptive emails or messages. These communications often contain links to fake websites that mimic real login pages, tricking users into entering their credentials.
To prevent phishing, always verify the authenticity of emails or messages asking for login details. Be wary of unsolicited communications and look for signs of phishing, such as misspellings, strange URLs, or unfamiliar senders. Educating employees on recognizing phishing attempts is essential to avoid falling victim to these scams.
Social Engineering: Manipulating Trust
Social engineering attacks leverage human psychology to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. Attackers might pose as IT support, colleagues, or even friends and family to manipulate victims into providing access or credentials.
Protecting against social engineering requires vigilance. Verify the identity of anyone requesting sensitive information, even if they seem familiar. Establish strict protocols for handling access requests and sharing sensitive data, ensuring employees know to question unexpected or suspicious requests.
The Business Impact of Credential Compromise
When credentials are compromised, the damage to a business can be severe, leading to financial loss, operational disruptions, and damage to its reputation.
Data Breaches and Financial Loss
One of the most immediate consequences of credential theft is a data breach, which can expose sensitive customer information, financial records, or intellectual property. The fallout includes financial losses from fraud or regulatory fines, along with the costly recovery process, which includes investigating the breach, notifying affected parties, and offering credit monitoring services.
Operational Disruptions
Compromised credentials can bring business operations to a halt. Attackers may use stolen login information to disable critical systems, steal data, or launch ransomware attacks that lock valuable files until a ransom is paid. These disruptions can cause significant downtime, affecting productivity and leading to lost revenue.
Reputational Damage
Data breaches and cyberattacks erode customer trust and can severely damage a business’s reputation. Customers may hesitate to continue doing business with a company that has suffered a breach, fearing that their personal data is at risk. Rebuilding trust can be a long and costly process, often requiring significant effort in public relations and customer engagement.
Best Practices to Protect Your Business from Credential Theft
Preventing credential theft involves a combination of robust security technology, clear policies, and employee awareness. Here are some best practices to help protect your business:
Enforce Strong Password Policies
Ensure employees use strong, unique passwords for every account and require regular updates. Passwords should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Consider implementing password managers to help employees store and generate secure passwords. A password expiration policy can further reduce the risk of long-term access from compromised credentials.
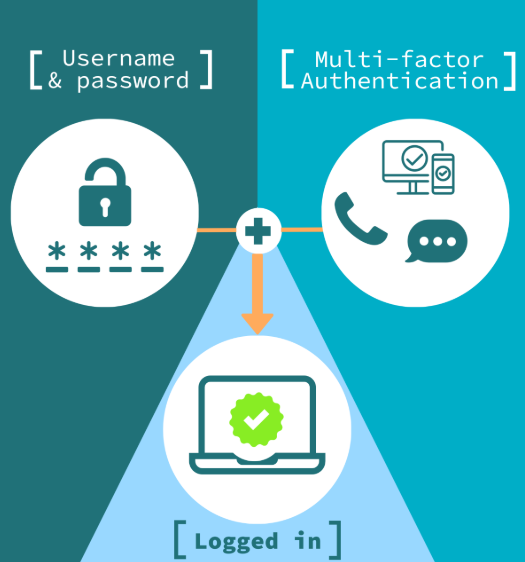
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA provides an added layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as one-time passwords (OTPs), biometric scans, or security keys. This makes it much harder for attackers to access systems, even if they have stolen a password. Prioritize MFA for critical systems and accounts, especially for sensitive financial data and cloud services.
Regular Security Awareness Training
Training your employees on cybersecurity best practices is one of the most effective defenses against credential theft. Provide regular training on recognizing phishing emails, avoiding social engineering tactics, and using secure passwords. Implement simulated phishing campaigns to test their responses and reinforce lessons learned.
Implement Access Controls
Limit access to sensitive data based on employees’ roles. This minimizes the impact of a credential compromise and ensures that employees only have access to the information they need. The principle of least privilege should be applied, and access permissions should be regularly reviewed to ensure they align with current responsibilities.
Keep Systems and Software Updated
Outdated software can be a major security risk, as it may contain vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Ensure your operating systems, applications, and security software are up-to-date with the latest patches and updates. Automated patching solutions can help ensure that all systems are consistently updated.
Monitor Network Activity
Regularly monitor your network for unusual activity that could indicate unauthorized access attempts. Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to gain real-time visibility into potential threats. These tools can help you quickly detect and respond to suspicious behavior before it leads to significant damage.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
Be prepared for potential security incidents by developing a comprehensive incident response plan. This plan should outline steps to contain breaches, notify affected parties, and recover data. Regularly test the plan with tabletop exercises to ensure your team can respond quickly and effectively during an actual attack.
Conclusion
Credential theft is a major cybersecurity threat, but with the right approach, businesses can significantly reduce their risk. By implementing strong password policies, enabling multi-factor authentication, educating employees, and staying vigilant about security, you can protect your organization from costly breaches and maintain the trust of your customers.