Managing unstructured data can be a daunting challenge for organizations, but it’s also one of the most important tasks to tackle. As the volume of unstructured data grows daily, businesses must learn how to store, manage, and leverage it effectively. In this post, we explore the best practices for handling unstructured data, including storage options such as databases and cloud solutions, while highlighting real-world examples of how organizations are putting these strategies into action.
Understanding Unstructured Data
Before diving into storage solutions, it’s important to grasp what unstructured data is. Unlike structured data, which fits neatly into tables and rows, unstructured data doesn’t follow a specific format or organizational model. This type of data includes everything from text documents and images to social media posts and videos, making it complex to manage and analyze.
Despite its unorganized nature, unstructured data holds tremendous potential. By implementing the right storage strategies, businesses can unlock valuable insights from this data and use it to inform decision-making, enhance customer experiences, and drive business innovation.
Using Databases for Unstructured Data Storage
While traditional databases were initially designed for structured data, they’ve evolved to support unstructured data as well. NoSQL and document-based databases, in particular, have become popular choices for storing unstructured data. These databases are more flexible than relational databases, allowing businesses to store data in various formats and retrieve it quickly.
Best Practices for Managing Unstructured Data in Databases
To effectively manage unstructured data in databases, companies should follow these best practices:
- Design Optimal Schemas: Tailor the database schema to suit the type of unstructured content being stored, ensuring scalability and efficiency.
- Optimize Queries: Use techniques like indexing to speed up data retrieval and minimize latency.
- Ensure Fast Access: With large volumes of unstructured data, it’s essential to have a robust search capability to locate and access the data when needed.
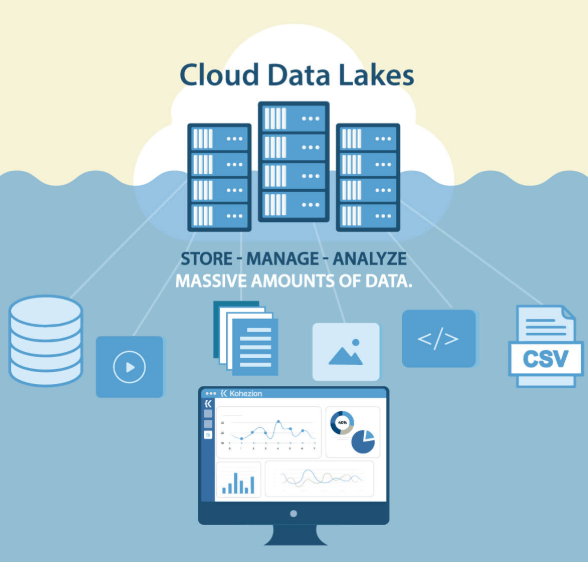
Cloud Storage for Unstructured Data
Cloud storage has revolutionized how businesses manage data, particularly unstructured data. Its vast scalability and ease of access make it an ideal solution for handling the complex and growing landscape of unstructured data. Cloud platforms provide the flexibility to store, process, and analyze data without the limitations of traditional on-premise storage solutions.
Why Cloud Solutions Are Ideal for Unstructured Data
Cloud storage offers several key advantages for managing unstructured data:
- Scalability: As data volumes grow, cloud storage can easily scale up or down, accommodating ever-changing data needs.
- Security: Cloud providers implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data from breaches and unauthorized access.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud storage eliminates the need for expensive on-site infrastructure, making it a cost-effective option for businesses.
Best Practices for Cloud-Based Unstructured Data Management
When using cloud storage to manage unstructured data, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Organize Data Based on Access Needs: Classify data to ensure that it’s organized for easy access and retrieval.
- Encrypt Data: Always encrypt data during storage and transfer to protect it from cyber threats.
- Utilize Automated Backups: Set up automated backup systems to ensure data is regularly saved and recoverable in case of an issue.
Real-World Examples of Unstructured Data Storage Solutions
Understanding how unstructured data storage works in practice is crucial. Here are a few examples of industries successfully leveraging these solutions:
Healthcare: A Data-Driven Revolution
In healthcare, unstructured data storage is crucial for managing patient records, imaging data, and research documents. By using a combination of databases and cloud storage, hospitals and research facilities can store and analyze this data to drive innovations in treatment and medical technology. This federated approach allows healthcare providers to harness vast amounts of unstructured data for breakthroughs in patient care.
Manufacturing: Embracing AI for Predictive Maintenance
The manufacturing industry is increasingly relying on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to improve operational efficiency. By storing schematics and operational data in databases and feeding real-time data from sensors and cameras into the cloud, manufacturers can use unstructured data for predictive maintenance and optimize production processes.
Media Industry: Managing Content Across Platforms
The media industry generates massive amounts of unstructured data in the form of audio, video, and digital content. By using NoSQL databases for managing content and cloud solutions for distribution and real-time analytics, media companies can streamline their content management processes and gain valuable insights into audience engagement.
The Future of Unstructured Data Storage
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the way we manage unstructured data. The future of unstructured data storage lies in the integration of cognitive computing, deep learning AI, and advanced analytics. These technologies will enable businesses to not only store data but also understand and learn from it in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Conclusion
Unstructured data is one of the most valuable resources businesses have, but it also presents unique challenges. By utilizing modern database solutions and cloud storage systems, companies can effectively manage, store, and analyze this data. With the right strategies and best practices in place, businesses can unlock the full potential of their unstructured data, driving innovation, improving efficiency, and gaining a competitive edge.