In today’s digital world, businesses manage an overwhelming amount of data, ranging from databases to emails, images, and videos. However, despite its increasing importance, data management remains a challenge for many organizations. Key gaps often exist in understanding data characteristics, automating policies, enabling reporting and audit functions, and managing the entire data lifecycle. Let’s dive into the five most significant challenges in data management and why they matter, especially when dealing with unstructured data, which accounts for more than 80% of enterprise data.
1. Understanding the Nature of Data
Every piece of data carries metadata, such as its origin, format, sensitivity, owner, and creation date. Structured data, like that found in relational databases, usually has these attributes clearly defined. However, unstructured data (such as PDFs, emails, and media files) can be much harder to manage because organizations often lack insights into its contents, ownership, and potential risks.
The Problem:
Many organizations fail to properly classify or tag unstructured data, leaving large amounts of it inaccessible and “dark.” Without understanding the characteristics of this data, managing it effectively, assessing its value, or ensuring compliance becomes almost impossible.
Why This Is Important:
Without proper metadata and classification, making informed business decisions becomes difficult. Risk assessments are compromised, and storage costs increase due to poor data management.
2. The Absence of Policy Automation for Compliance, Security, and Retention
Data management policies are essential to determine how long to retain data, how to secure it, and how to comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Automating these policies ensures they are applied consistently across all types of data and systems.
The Problem:
Many organizations rely on outdated or manual processes that fail to apply these policies to unstructured data stored in file shares, cloud platforms, and endpoints. While structured data systems like CRMs and databases often have built-in controls, unstructured data systems lack similar mechanisms.
Why This Is Important:
Without automation, companies risk non-compliance, data breaches, and storing unnecessary data, which leads to higher costs and potential legal problems.
3. Limited Reporting Capabilities
Reporting plays a crucial role in understanding your data’s status—where it’s stored, who has access to it, and how it evolves over time.
The Problem:
While structured data typically has detailed reporting, unstructured data lacks similar visibility. File systems and collaboration tools don’t usually provide comprehensive reporting options, making it difficult to track data growth, access patterns, or potential risks.
Why This Is Important:
Without effective reporting, organizations can’t properly monitor or manage their data. This lack of insight leads to potential security breaches, inefficiency, and poor strategic planning.
4. Difficulty in Auditing Data Access and Usage
Auditing ensures transparency by tracking who accesses or modifies data, when, and what changes are made. This is vital for security, governance, and compliance.
The Problem:
While auditing is standard for structured data in databases, it’s often not available for unstructured data, especially in legacy systems or decentralized cloud storage. Even when audit logs do exist, they’re often not centralized or easy to search.
Why This Is Important:
Without an auditing process, detecting unauthorized access becomes nearly impossible, and organizations face challenges in responding to incidents or proving compliance during audits.
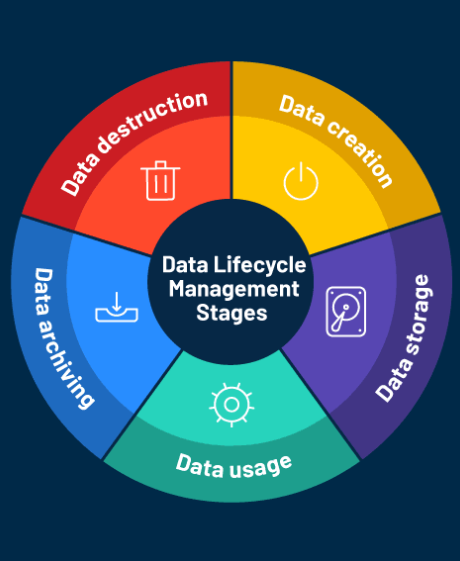
5. Disjointed Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management (DLM) ensures that data is controlled from its creation to archiving and eventual deletion, ensuring it remains secure, useful, and compliant.
The Problem:
Many organizations fail to implement a unified approach to managing the lifecycle of unstructured data. As a result, files remain long after they’re no longer needed, occupying storage and creating risk. While structured data often benefits from more disciplined management, gaps still exist, especially due to siloed systems.
Why This Is Important:
Without a clear process in place, companies either hold onto data indefinitely or delete it too soon—both practices are risky and unsustainable.
Addressing the Gaps with a Comprehensive Solution
Effective data management isn’t just about staying organized; it’s about minimizing risks, reducing costs, and unlocking the true potential of your data. The primary challenges in data management arise from poor visibility, manual processes, and fragmented tools, particularly when managing unstructured data.
To overcome these challenges, businesses need a comprehensive data management solution that:
- Classifies and identifies all types of data
- Automates retention, compliance, and security policies
- Provides detailed reporting and audit trails
- Manages the entire data lifecycle from creation to deletion
Don’t allow data to become a liability. By addressing these gaps with a robust solution, you can better manage the complexity and compliance demands of modern data environments.